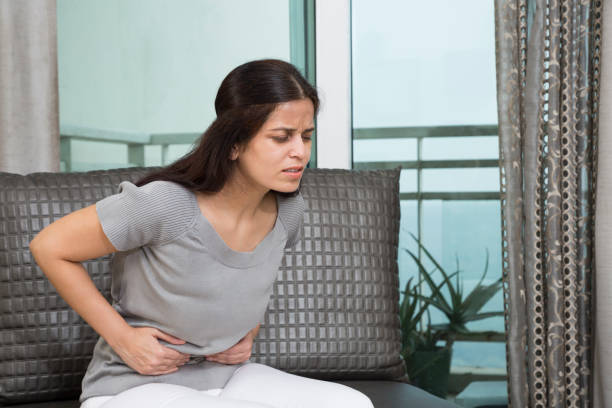
Vitamin B12 is an essential substance that plays a vital role in brain function, red blood cell production, and nervous system maintenance. Despite its importance, the human body does not produce it , so it must be obtained through diet.
In this guide, we’ll explore the crucial functions of vitamin B12 and its natural sources, such as meat, fish, and dairy. We’ll also address the consequences of your B12 deficiency and outline options for vegetarians and vegans who need to supplement this essential vitamin.
What is vitamin B12 and how important is it for health?
Vitamin B12 , also known as cobalamin , is a water-soluble vitamin. It plays a key role in the functioning of the brain and nervous system , the formation of red blood cells , the regulation of metabolism, and the extraction of energy from food.
It is part of the vitamin B complex and is found in animal foods such as meat, fish, eggs and dairy products. Its absence can cause serious health problems, such as anemia and neurological damage.
It is essential because the body cannot produce it , so it must be obtained through diet or supplementation. Its importance also lies in its role in DNA synthesis and tissue renewal . Its deficiency can lead to a variety of health problems, so making sure you get enough is crucial.
Functions and benefits of vitamin B12 in the body
Vitamin B12 is essential for many functions in the body, and offers a variety of essential benefits, including:
- Red Blood Cell Production: Facilitates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow and prevents megaloblastic anemia.
- Neurological Function: It is vital for the health of the nervous system, maintaining healthy nerve cells, and helping in the transmission of nerve signals.
- Protein and Fat Metabolism: Plays an important role in the metabolism of proteins and fats, transforming them into energy.
- DNA synthesis: It is essential in the process of DNA replication and repair, ensuring normal cellular function.
- Heart Health: Helps lower levels of homocysteine, an amino acid associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
Cobalamin not only plays a role in key functions in the body. It also works in conjunction with other B vitamins to form red blood cells, improve immune function, and boost mood .
Below you will find a table highlighting 12 foods rich in vitamin B12 , an essential guide to ensuring adequate intake through diet:
Vitamin B12 content (micrograms per 100g)
1.Calf Liver: 111
2.Clams: 98
3.Sardines: 8.9
4.Trout: 5.4
5.Tuna: 4.9
6.Egg(Yolk): 2.7
7.Swiss Cheese: 3.3
8.Milk: 1.2
Recommendations for incorporating foods with vitamin B12 into your daily diet
Incorporating vitamin B12 into your diet is essential for your health. Here are some helpful tips:
- Include fatty fish such as salmon and trout in weekly meals.
- Consume dairy products such as milk and yogurt, which are easy and accessible sources.
- Add eggs to your breakfast or salads , as the yolk contains this vital vitamin.
- For vegetarians and vegans, consider B12 supplements or fortified foods such as cereals and plant-based milks.
- For those with an aversion to animal products, look for products fortified with vitamin B12 . For example, some varieties of soy or almond milk.
- Opt for lean cuts of meat , such as chicken breast or calf liver, which are excellent sources.
- Incorporate seafood, such as clams and crabs, into your diet.
- Consult a healthcare professional for a personalized diet plan to ensure adequate B12 intake.
- Consider periodic blood testing to monitor cobalamin levels, especially if you have a restricted diet or medical conditions that may affect absorption.
For Proper dosage you may contact us at:
+91 9266782222
+91 9711224402